Exercise 4 - Don’t Crash! Tailing Behaviour
In this exercise we implement an autonomous safe tailing behavior on our Duckiebot. We aim to tail another Duckiebot at a safe distance while still following the rules of the road. This lab was a hard sprint right from the start. Despite the overall implementation being much more obvious than the straightforward than all previous labs, we experienced many difficulties stemming from the real-time nature of this lab.
A video of our Duckiebot safely driving around the town behind another Duckiebot (controlled with keyboard controls). Observe our Duckiebot taking a right hand turn and left hand turn at the intersections and driving at least two full laps of the town. “It was just a fluke”
Strategy
Our strategy centres around a state machine. We use the following states:
- Lane Following: Runs lane following node. This is the default when we lose track of the bot ahead
- Stopping: We approach a red line and come to a halt. While we wait, we look for a bot ahead of us to decide which way to turn
- Tracking: We follow the robot in front of us
- Blind movements: We override the lane following to force a turn/forward across the intersection to follow the bot based on where we observed it turning while stopped
Our state machine starts off lane following, then switches to tracking when it sees the bot and back when it loses it. The stopping state takes precedence over both of these states, so the bot will unconditionally stop when seeing a red line. The blind states only last for a few seconds each, though also get a “stop immunity” where the bot ignores all red lines. This is important when going through an intersection, otherwise we’d stop in the middle of the intersection by seeing the red line from the other line.
Check out the diagram below!
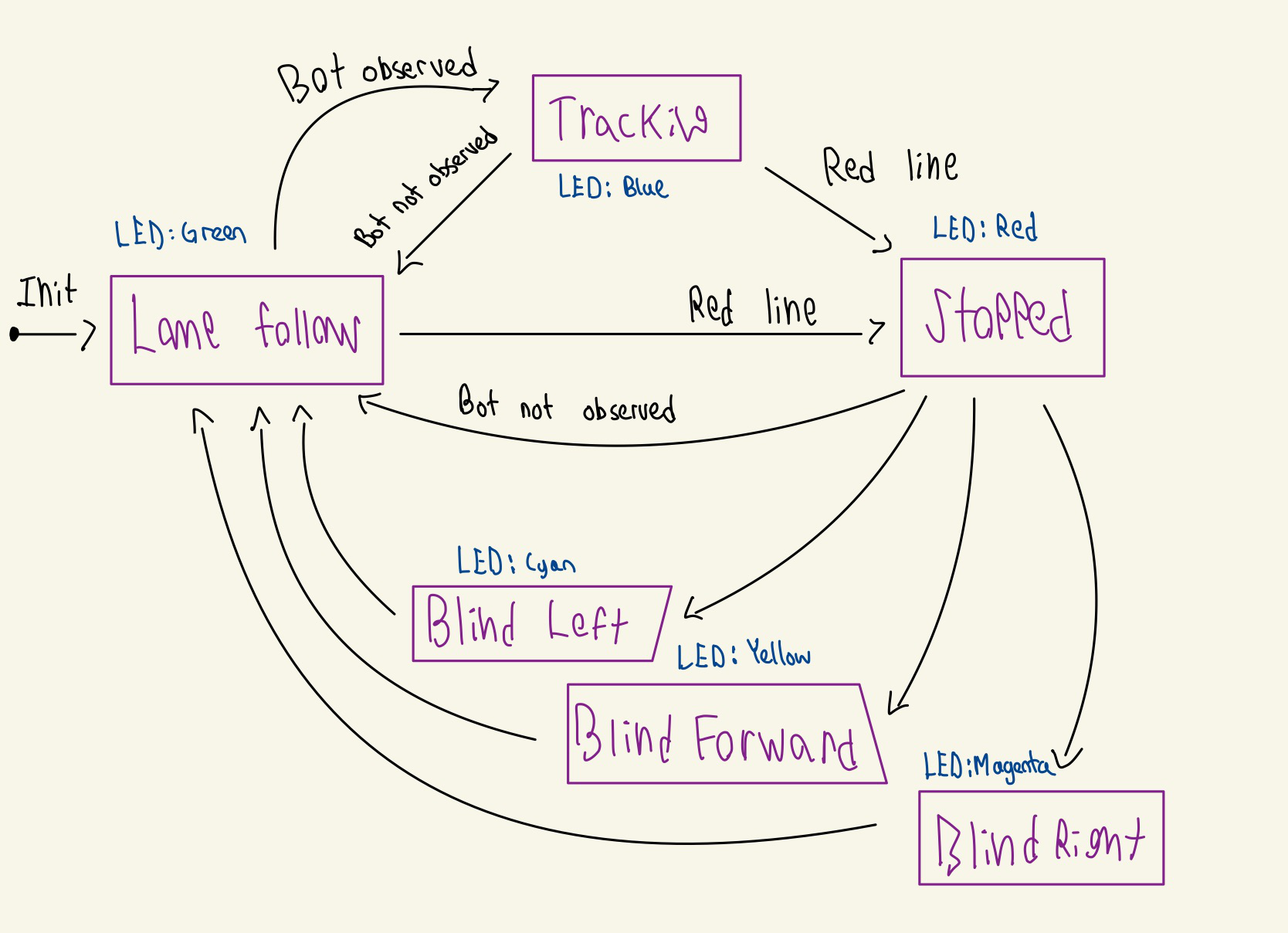
Our LEDs sort of indicate the state… though they’re very delayed sometimes due to duckiebot driver issues, so take them with a grain of salt. Blue only happens when the bot stops or moves backward while tracking.
Aside from the contour-masking code for the yellow lane from the previous lab, the new sensors in this one come from
- Detecting the grid on the back of another Duckiebot
- Using the time-of-flight (TOF) sensor to detect distance
We initially struggled to get the TOF to integrate well with the distance transform we were getting from the grid-tracking-camera node. As the Duckiebot detection node is intermittent, we had to use the TOF to fill in the gaps, however, we noticed that the two measurements did not perfectly correspond.
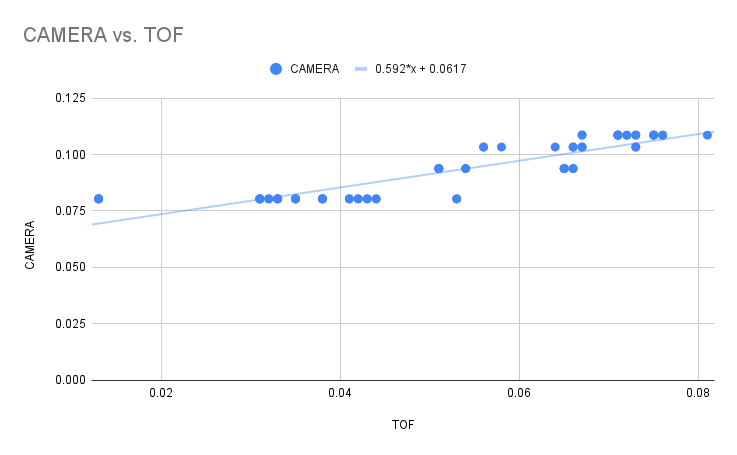
To resolve this discrepancy, we plotted them against each other and fitted a line to the points. Using the slope, of this line, we were able to convert between both measurements, allowing us to fuse both sensors. We found TOF particularly important at close distances, where the camera could no longer fully see the grid on the back. The camera provided a far great field-of-view, which is exactly when the TOF lost distance measures, so the two sensors were able to cover for the weaknesses of the other. When both were sensing, we took the minimum to get an conservative measurement of distance.
Discussion
Our Duckiebot managed to follow the bot ahead very nicely in a straight line. When it wasn’t lagging, the LEDs provided a great way to introspect our state, which made it much easier for the person doing keyboard_control on the bot in front. With extensive tuning, our PID stopped the wobbles and kicks coming from the P and D terms respectively.
The biggest challenge were the turns at the intersections. Here, our bot had to keep a backlog of the latest positions its seen from the bot ahead, while also making sure none of those measurements are irregular or stale. We modified our detection publisher to publish the entire transformation matrix from the camera to the grid on the back, which let see the angle in the pose of the grid. Using this information, we could predict which direction the bot in front of us turned or if it had gone forward.
How well did your implemented strategy work?
Our implemented strategy worked pretty well, it successfully fulfilled the requirements for the video, also it can reverse when the tracked Duckiebot starts to reverse!
Was it reliable?
Overall our strategy was fairly reliable, as it’s able to drive around the town without crashing into other Duckiebots and tail another Duckiebot autonomously at a safe distance. Furthermore, it also follows the rules of the road by driving within the lanes, stays on the right side of the road, stopping at intersections, and blinking the appropriate rear LED to signal turns.
In what situations did it perform poorly?
Sometimes, our Duckiebot detection node fails to detect the tracked bot making a turn at an intersection. This especially happens on sharp turns, where the node might only detect the bot at a frame right before the bot ahead turns and assume the bot went straight. This makes us lose any information about the angle the bot ahead turned at, which makes it hard to plan a turn, so we default to lane following in these uncertain times.